Machine Learning
Contents
Machine Learning#
General Machine Learning Concept#
Simplified: in machine learning, a computer is trained to classify new data. Think of it as an input-output device that takes in a number of inputs, and based on the pattern of these inputs, determine the most likely class associated with that data. There two main types of learning strategies. 1) Supervised learning where you train the machine using data for which the correct class is known. 2) Unsupervised learning where the classifier itself tries to find patterns within the input data itself. (Biosignal and Medical Image Processing John Semmlow)
Classification (determine
label) vs Regression (predict anumerical value)
General Outline of Machine Learning#
Loading Data
Load toy data included in sklearn
Download published/annotated data from online
Generate data with specific statistics to learn how algorithms work
Preprocessing Data
Make data zero mean
Make data unit variance
Fix range of values
Deal with missing values
Map text labels to integer labels (if applicable) – ML algorithms require the data be numeric
Dimensionality Reduction of data
If you use too many features and do not have enough samples, you could over fit.
So you have to choose the most discriminating few features
Applying algorithms
Labeled Data - Supervised
Non-labeled Data - Unsupervised
Evaluation
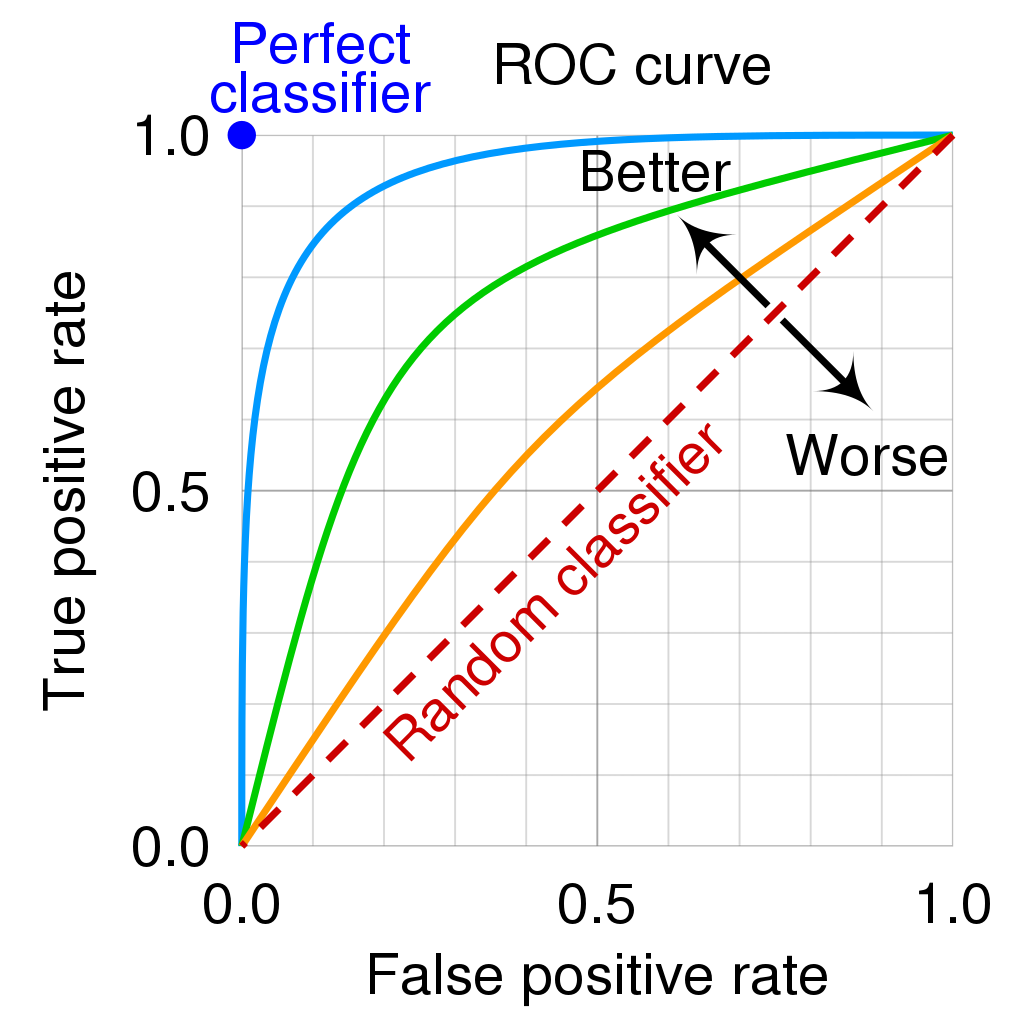
Receiver Operator Curve
Sensitivity
Specificity
Imbalanced Data
Example: 95 % one class, 5% another class
REF: Scikit-learn Essentials: Mastering the scikit-learn Machine Learning Library for Python by Dhiraj Kumar
Various Python Libraries: When to use what#
Numpy – provides efficient array computation via vectorization and broadcasting
Vectorization – no need for explicit looping – example, vector multiplication or squaring
Broadcasting – manipulate multiple values at once
Pandas - Uses Numpy arrays as the underlying structure. Good for analyzing tabular data
Scipy (scientific python)- provides libraries for scientific computing, including: integration, interpolation, signal processing, linear algebra, statistics. Also uses Numpy infrastructure
Scikit-learn - provides a collection of machine-learning algorithms that use Numy and Scipy
Most used Python library for machine-learning
regression
classification
clustering
Topics Covered#
Introduction to Scikit-learn
Loading Dataset using Scikit-learn
Preprocessing data using scikit-learn
Train Test split using scikit-learn
Linear regression using scikit-learn
Naive Bays using Scikit learn
SVM using Scikit learn
k-Nearest neighbor using Scikit-learn
Introduction to Scikit-learn#
Choose the right estimator – the right algorithm for doing ML
Consistent – all object share a common interface
Inspection – all parameter values are exposed as public attributes
Limited object Hierarchy – algorithms are represented as Python classes, datasets mainly as numpy array and parameters as standard python strings
Composition – ML as a sequences of fundamental algorithms
Defaults – provides good default values
High Level Steps#
Choose the class of model to be coded
Choose the hyper parameters of the model
Arrange data into target and features
Write model fitment code using fit() method.
General Steps#
Load Data
Three ways load data
Dataset loaders (toy datasets that come with skikit-learn)
Good for illustrating how the various algorithms work
Dataset fetchers (real world datasets)
Built-in functions to load large datasets
Pull from openml.org
Dataset generation functions
Artificial datasets – can create labeled datasets
Pre-process Data
Remove mean **
Scale Variance **
Non-linear transformation
Normalization
Encoding categorical features
Discretization
Imputation of missing values
Maybe remove outliers if it can be justified. Always document this in research paper
Loading data#
Preprocessing#
Mean and Variance#
algorithms require that all the features have variance of similar magnitude. If the magnitude differ by orders of magnitude larger than others, it might dominate the objective function.
Whatever mean or std you subtract from the training set, you have to use the same on the testing set.
Algorithms assume that the input data is Gaussian distribution with zero mean and unit variance.
Power transformers aim to map data from any distribution to as close to a Gaussian distribution
Encoding#
Map text values to integer codes. For example, instead of using text for city names, use integers, or Male = 0, Female = 1. This allows fitting numerical values into models.
Discretization#
Turn continuous values in to discrete values. You bin the continuous into bins. *** Linear models can become non-linear due to discretization
Imputation#
Many real world datasets contain missing values;
Discard entire rows
Or fill data – usually by guessing from available data
Splitting Data#
It is common to split data into training and testing samples.
Usually you do 90/10 or 80/20.
The splitting has to be random
K-Cross-fold validation – split data K times
Linear Regression#
LR models the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variable. When one increase or decrease, the other increases or decreases.
Naive Bayes#
Simple supervised machine learning classifier
Assumes the features are independent
Example – apple is red, round and 4 cm in diameter
Support Vector Machine (SVM)#
Another supervised machine learning classifier
use for both classification and regression
Can do non-linear classification
Hyper plane – maximize the margin between two classes
Support Vectors – data points that define the hyper plane
Margin width – define an optimal hyper plane we need to maximize the width of the margin